Forfaiting Explained: A Key Financing Solution for International Trade
Content
- What Is Forfaiting?
- Key Features of Forfaiting:
- How Does Forfaiting Work?
- Who Can Benefit from Forfaiting?
- Benefits of Forfaiting
- Challenges of Forfaiting
- Industries That Use Forfaiting
- Real-World Example: Forfaiting in Action
- How to Use Forfaiting Strategically
- Tips for Choosing a Forfaiting Partner
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
Over the past few years, trade tensions between major economies—such as the U.S. and China, the U.S. and the European Union, and other countries—have made global trade more challenging. In this complex world of international trade, businesses often face difficulties related to delayed payments, currency risks, and credit exposure. Forfaiting is a financing solution that addresses these concerns, providing exporters with immediate cash flow while transferring payment risks to a forfaiter.
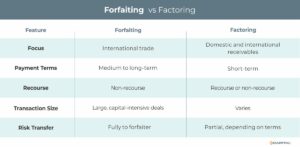
In many ways, forfaiting is akin to invoice factoring. Both financing solutions simplify trade transactions and accelerate cash flow to benefit the seller with little to no impact on the buyer. The difference lies in scale and complexity. An exporter would typically choose forfaiting over invoice factoring when dealing with large, long-term international transactions, where non-recourse protection, a focus on reducing risk, and offloading long-term receivables are priorities.
This blog explores forfaiting, how it works, its benefits, and why it’s an essential tool for businesses engaged in international trade.
What Is Forfaiting?
Forfaiting is a trade financing mechanism where an exporter sells its receivables—usually in the form of promissory notes or bills of exchange—to a forfaiter at a discount. The forfaiter assumes the payment risk, enabling the exporter to receive immediate cash and eliminate concerns about credit or geopolitical risks.
Key Features of Forfaiting:
- Non-Recourse: The forfaiter bears the credit and payment risks.
- Immediate Liquidity: Exporters receive upfront payment for receivables.
- International Trade Focus: Primarily used in cross-border transactions involving medium- to long-term payment terms.
How Does Forfaiting Work?
- Trade Agreement: The exporter and importer agree on the terms of the trade transaction, with payment often structured through deferred receivables like promissory notes or bills of exchange.
- Receivables Sale: The exporter sells the receivables to a forfaiter, typically a financial institution or specialized financing company.
- Discounted Payment: The forfaiter pays the exporter the value of the receivables, minus a discount that accounts for interest and fees.
- Risk Transfer: The forfaiter assumes the responsibility of collecting payment from the importer, including the associated credit and political risks.
- Repayment: The importer makes payment directly to the forfaiter as per the agreed terms.
Who Can Benefit from Forfaiting?
Forfaiting is ideal for:
- Exporters: Looking to improve cash flow and reduce credit exposure in international transactions.
- Importers: Gaining flexibility in payment terms without straining supplier relationships.
- Businesses in Emerging Markets: Managing risks associated with currency fluctuations and political instability.
- Industries with Capital-Intensive Exports: Such as machinery, infrastructure, or large equipment sales.
Benefits of Forfaiting
- Immediate Cash Flow
- Exporters receive upfront payment, improving liquidity and enabling reinvestment in operations.
- Risk Mitigation
- Shifts credit, payment, and political risks to the forfaiter, protecting exporters from non-payment.
- Simplifies Transactions
- Streamlines complex international trade processes, making it easier to manage deferred payment terms.
- Enhances Competitiveness
- Allows exporters to offer attractive payment terms to importers without taking on additional risk.
- Non-Recourse Financing
- Exporters are not liable if the importer defaults, providing peace of mind.
- Currency Risk Management
- Forfaiting can include hedging against exchange rate fluctuations in cross-border transactions.
Challenges of Forfaiting
- Cost of Discounting
- The forfaiter charges fees and interest, which can reduce the overall value of receivables. Smaller, less complex deals may be better serviced by using invoice factoring.
- Transaction Size Requirements
- This type of financing is typically used for large-scale transactions, limiting its accessibility for smaller deals.
- Documentation Complexity
- Requires well-structured documentation, including promissory notes or bills of exchange.
- Limited Applicability
- Best suited for specific industries or trade scenarios involving deferred payments.
Industries That Use Forfaiting
- Machinery and Equipment
- Exporters of large-scale industrial or manufacturing equipment.
- Construction and Infrastructure
- Companies involved in international infrastructure development projects.
- Aerospace and Defense
- For aircraft, defense equipment, or specialized technology exports.
- Energy
- Exporters of power generation equipment or renewable energy technologies.
- Pharmaceuticals
- For large-scale shipments to international buyers with extended payment terms.
Real-World Example: Forfaiting in Action
Scenario: A European machinery manufacturer receives a $2 million order from an importer in an emerging market. The importer requests deferred payment terms over 18 months, but the exporter needs immediate funds to manage production costs.
Solution: The exporter sells the receivables to a forfaiter at a 5% discount, receiving $1.9 million upfront. The forfaiter assumes the risk of collecting the $2 million from the importer over the payment term.
Outcome: The exporter improves cash flow and avoids credit risks, while the importer benefits from extended payment terms, ensuring a win-win situation.
How to Use Forfaiting Strategically
- Evaluate Transaction Size
- Use this type of financing for large transactions where payment terms exceed six months.
- Partner with Reputable Forfaiters
- Work with experienced forfaiters who understand your industry and trade markets.
- Ensure Strong Documentation
- Prepare accurate and enforceable receivables to simplify the forfaiting process.
- Align with Risk Management Goals
- Use forfaiting to mitigate exposure to high-risk markets or credit uncertainties.
- Incorporate Currency Hedging
- Include currency risk management to stabilize receivables in volatile markets.
Tips for Choosing a Forfaiting Partner
- Global Expertise
- Select forfaiters with knowledge of international trade and geopolitical risks.
- Transparent Fees
- Ensure clear communication about discount rates, interest, and fees.
- Flexibility
- Look for forfaiters that accommodate diverse trade structures and industries.
- Customer Support
- Choose partners offering responsive service and tailored solutions.
- Reputation
- Verify the forfaiter’s track record and reliability through client reviews or industry references.
Conclusion
Forfaiting is an invaluable financing tool for businesses engaged in international trade. By converting receivables into immediate cash and transferring payment risks to a forfaiter, it enables exporters to focus on growth, streamline operations, and enhance competitiveness in the global market.
If your business deals with large, cross-border transactions and deferred payment terms, this financing strategy could be the solution you need. Partner with experienced forfaiters, align your trade goals, and use this strategic financing tool to simplify trade and secure financial stability.
Contact us to assess your company’s best approach to overcome cash flow constraints, whether your business deals with large and complex international trade arrangements or smaller, more frequent domestic deals.
Key Takeaways
- In the complex world of international trade, businesses often face difficulties related to delayed payments, currency risks, and credit exposure.
- Forfaiting is a trade financing mechanism where an exporter sells its receivables to a forfaiter at a discount. The forfaiter assumes the payment risk, enabling the exporter to receive immediate cash and eliminate concerns about credit or geopolitical risks.
- This financing strategy enables exporters to focus on growth, streamline operations, and enhance competitiveness in the global market.
ABOUT eCapital
At eCapital, we accelerate business growth by delivering fast, flexible access to capital through cutting-edge technology and deep industry insight.
Across North America and the U.K., we’ve redefined how small and medium-sized businesses access funding—eliminating friction, speeding approvals, and empowering clients with access to the capital they need to move forward. With the capacity to fund facilities from $5 million to $250 million, we support a wide range of business needs at every stage.
With a powerful blend of innovation, scalability, and personalized service, we’re not just a funding provider, we’re a strategic partner built for what’s next.